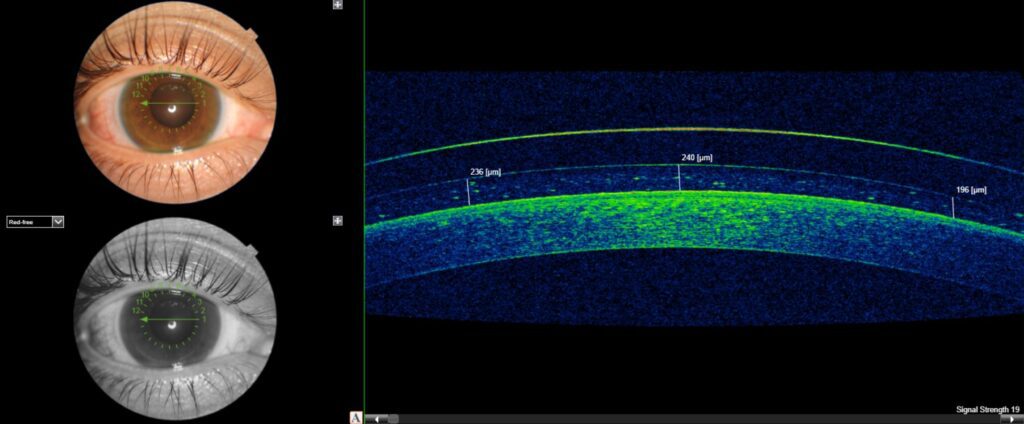
In the January 2023 edition of Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Maria Walker et al. examined scleral lens midday fogging (MDF) in 26 eyes of 13 neophyte Europa scleral lens wearers. Quantification of MDF was achieved by analyzing AS-OCT images. Samples of the fluid reservoir were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Turbidity of Fluid Reservoir:
Dr. Walker’s team evaluated the fit and clearance after 8 hours of wear on day 1 and day 4. MDF was analyzed by using mean gray value in calibrated optical units from the AS-OCT images and found on day 1 there was 33 ± 29 units and 28 ± 24 units on day 4 (scale was out of 100) which was statistically significant. Fogging was also graded on a scale of 1-5 subjectively by subjects where ≤ 3 was considered a non-MDF score. Subjective and objective measurements agreed.
Figure 1. Debris found within the fluid reservoir of a lens with adequate central clearance. (Image courtesy of Jenny Wong, OD)
What about the fit?
The subjects were scanned with profilometry (sMap) and Europa lenses were designed. Of the 13 participants, 9 were fit with 16.0 mm, 1 fit with 15.5 mm, 1 fit with 16.2 mm and 2 fit with 16.5 mm diameter lenses. Haptic toricity was utilized in 18 (~70%) lenses with an average toricity of 127 ± 114 µm. The initial clearance was approximately 300 microns with average settling of 81 ± 75 µm on day 1 and 88 ± 42 µm on day 4. One eye of 26 had settled 240 µm and had no clearance and was not studied. They found no correlation between the lens parameters (clearance, settling, or toricity) and MDF.
What’s the fogging made of?
Twelve pooled samples (7 from those that had MDF and 5 from those that did not) were analyzed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. The lipid concentration was 31.0 ± 9.3 µg/ml in the MDF group and 33.0 ± 13.9 µg/ml in the non-MDF group. There were 170 lipids that were detected including sterols, fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids. Glycerolipids were more prominent in the MDF samples (26%) than the non-MDF samples (2%). Fatty acyl lipids were found more in the MDF group than the non-MDF group (8% vs <1%); Sterol lipids were found in 4% of lipids in the MDF group compared to <1% of non-MDF. Interestingly, glycerophospholipids were the predominant lipid in both groups but were 90% in non-MDF and 58% in the MDF group.
So, what does this mean?
MDF is comprised of many lipid classes and nonpolar hydrophobic lipids were the most common in MDF in this cohort of normal subjects. Wax esters secreted by Meibomian glands were highly correlated with MDF. There was no correlation with polar lipids and MDF, but they were still present. These polar lipids may arise from cellular debris since they are commonly found in cellular membranes which may warrant further investigation. It was suggested that more lipophilic solution in the reservoir may act to reduce precipitation of the nonpolar lipids. This was not studied but may provide a clinical tool to help this frustrating problem.
Walker MK, Bailey LS, Basso KB, Redfern RR. Nonpolar Lipids Contribute to Midday Fogging During Scleral Lens Wear. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Jan 3;64(1):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.1.7. PMID: 36630141; PMCID: PMC9840443.